|
Mastering Herpes Zoster: A Comprehensive Guide for Nephrologists
This module aims to empower nephrologists with a comprehensive understanding of Herpes Zoster (HZ), its implications for patients with kidney diseases, and the latest strategies for its management and prevention. To enhance patient outcomes and promote a culture of continuous improvement in the management and prevention of HZ in patients with kidney diseases.
Learning Objectives: Upon completion of this module, you should be able to: 1. Describe the background of HZ including its clinical manifestations and the role of declined immunity in HZ infection. 2. Identify the risk factors and complications of HZ and understand their cost implications. 3. Recognize the burden of HZ in the general population and its link with kidney diseases. 4. Identify the types of HZ vaccines and the approach to vaccination. 6. Explain the profile, clinical efficacy, immunogenicity, and safety of the Recombinant Zoster Vaccine (RZV). 7. Explore the local guidelines for RZV in KSA and international recommendations for RZV. |
|
Mastering Herpes Zoster: A Comprehensive Guide for Diabetologists
This module aims to empower diabetologists with a comprehensive understanding of Herpes Zoster (HZ), its implications for diabetic patients, and the latest strategies for its management and prevention. To enhance patient outcomes and promote a culture of continuous improvement in the management and prevention of HZ in diabetic patients.
Learning Objectives: Upon completion of this module, you should be able to: 1. Describe the background of HZ including its clinical manifestations and the role of declined immunity in HZ infection. 2. Identify the risk factors and complications of HZ and understand their cost implications. 3. Recognize the burden of HZ in the general population and its link with diabetes mellitus. 4. Identify the types of HZ vaccines and the approach to vaccination. 6. Explain the profile, clinical efficacy, immunogenicity, and safety of the Recombinant Zoster Vaccine (RZV). 7. Explore the local guidelines for RZV in KSA and international recommendations for RZV. |
|
Mastering Herpes Zoster: A Comprehensive Guide for Cardiologists
This module aims to empower cardiologists with a comprehensive understanding of Herpes Zoster (HZ), its implications for cardiac patients, and the latest strategies for its management and prevention. To enhance patient outcomes and promote a culture of continuous improvement in the management and prevention of HZ in cardiac patients.
Learning Objectives: Upon completion of this module, you should be able to: 1. Describe the background of HZ including its clinical manifestations and the role of declined immunity in HZ infection. 2. Identify the risk factors and complications of HZ and understand their cost implications. 3. Recognize the burden of HZ in the general population and its link with cardiac diseases. 4. Identify the types of HZ vaccines and the approach to vaccination. 6. Explain the profile, clinical efficacy, immunogenicity, and safety of the Recombinant Zoster Vaccine (RZV). 7. Explore the local guidelines for RZV in KSA and international recommendations for RZV. |
|
Hemorrhoids and Associated Anal Fissures Therapeutics
Hemorrhoid disease (HD) is a prevalent anorectal condition, particularly in the industrialized world, that significantly affects patients’ quality of life.
This disease, which has been recognized for centuries, is considered benign. However, it carries a substantial social impact due to the wide range of symptoms that can be associated with it, both by patients and physicians. This has led to increased interest in understanding HD from a diagnostic and therapeutic standpoint. It’s important to note that various gastrointestinal disorders can produce symptoms similar to those of hemorrhoids, some of which can be life-threatening. Therefore, this module aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the evaluation and management of HD, emphasizing the importance of accurate diagnosis. Learning objectives By the end of this module, you should be able to:
|
|
Acute Diarrhea Enhancing Clinical practice
This e-learning module is a comprehensive guide designed to empower pharmacists in the effective management of acute diarrhea. It provides an in-depth understanding of acute diarrhea, its various types, causes, and global impact.
The module emphasizes the crucial role of pharmacists in disease evaluation, patient history gathering, recognizing alarming signs, and making appropriate referrals. It outlines the importance of supportive treatment, symptomatic treatment, and the role of antibiotics in acute diarrhea. The module also introduces complementary treatments such as probiotics and zinc supplementation. A significant portion of the module is dedicated to Racecadotril, an antisecretory agent used in the management of acute diarrhea, discussing its indications, mechanism of action, efficacy, safety, administration recommendations, contraindications, and precautions. The module aims to equip pharmacists with the knowledge and skills to handle different cases of acute diarrhea, prescribe suitable medications, and provide patient-oriented care. Learning Objectives: By the end of this module, you should be able to:
|
|
Case 01: Meet the Challenge and Manage Saleh’s Case
This learning activity is an engaging, video-based module that revolves around a medical case. The case involves a patient named Saleh, who is dealing with a health issue. The activity is designed to be a choose-your-own-adventure style learning experience, where your decisions can impact the recovery of the patient.
Learning Objectives: By the end of this e-Learning movie, you should be able to:
|
|
Case 02: Are You Ready To Help Wajd’s and Her Son’s Journey To Recovery?
This learning activity is a video-based, interactive experience that revolves around a medical case. The case involves a patient named Wajd and her son, both of whom are dealing with a health issue. The activity is designed to be a choose-your-own-adventure style learning experience, where your decisions can impact the recovery of the patients.
Learning Objectives: By the end of this e-Learning movie, you should be able to:
|
|
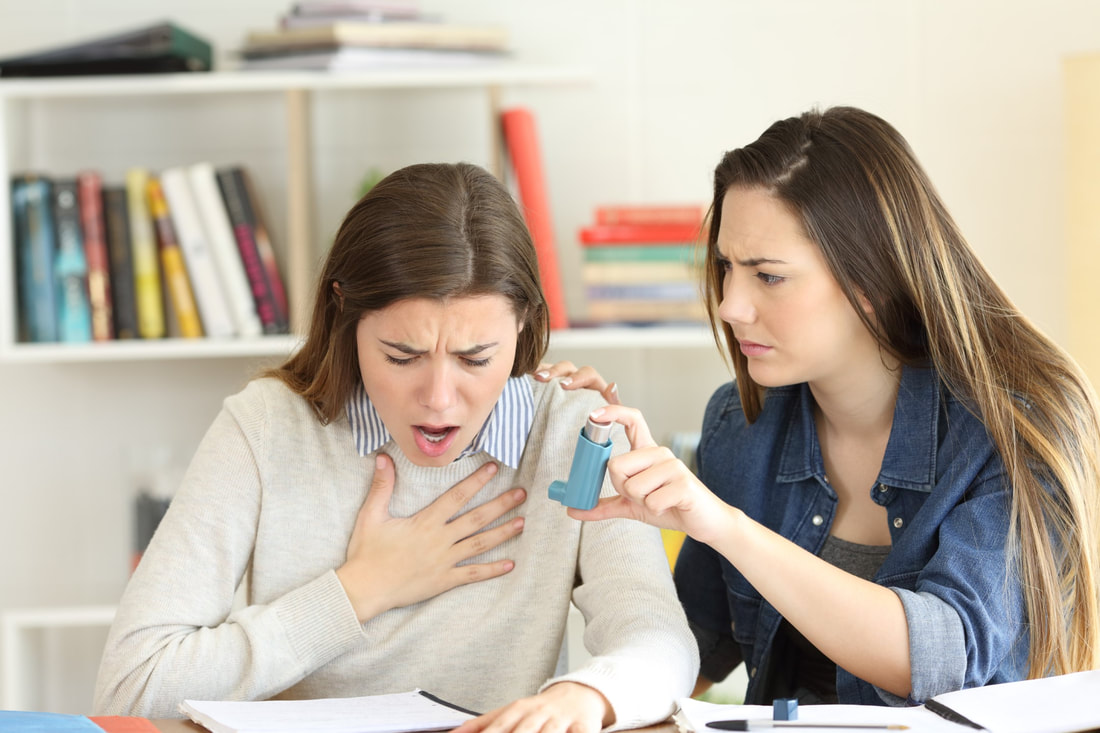
Case 04: Undertake the Uncertainty and Assess Bandar’s Asthma
This e-learning activity is an immersive, video-guided journey that centers on a medical scenario. The case features a patient named Bandar, who is navigating a medical condition challenge. This activity is structured as an interactive branching-path, where your choices can influence the decision of the patient’s case.
Learning Objectives: By the end of this e-Learning movie, you should be able to:
|
|
Case 05: Are You Prepared to Tailor Bandar Asthma Management Plan?
This e-learning activity is a video-based, interactive experience that takes place in a special medical department meeting. The discussion about asthma management for a patient called Bandar. The activity is designed as a dynamic learning experience, where you explore various aspects of patient care and medical decision-making, enriching your understanding of Bandar’s health condition.
Learning Objectives: By the end of this e-Learning movie, you should be able to:
|
|
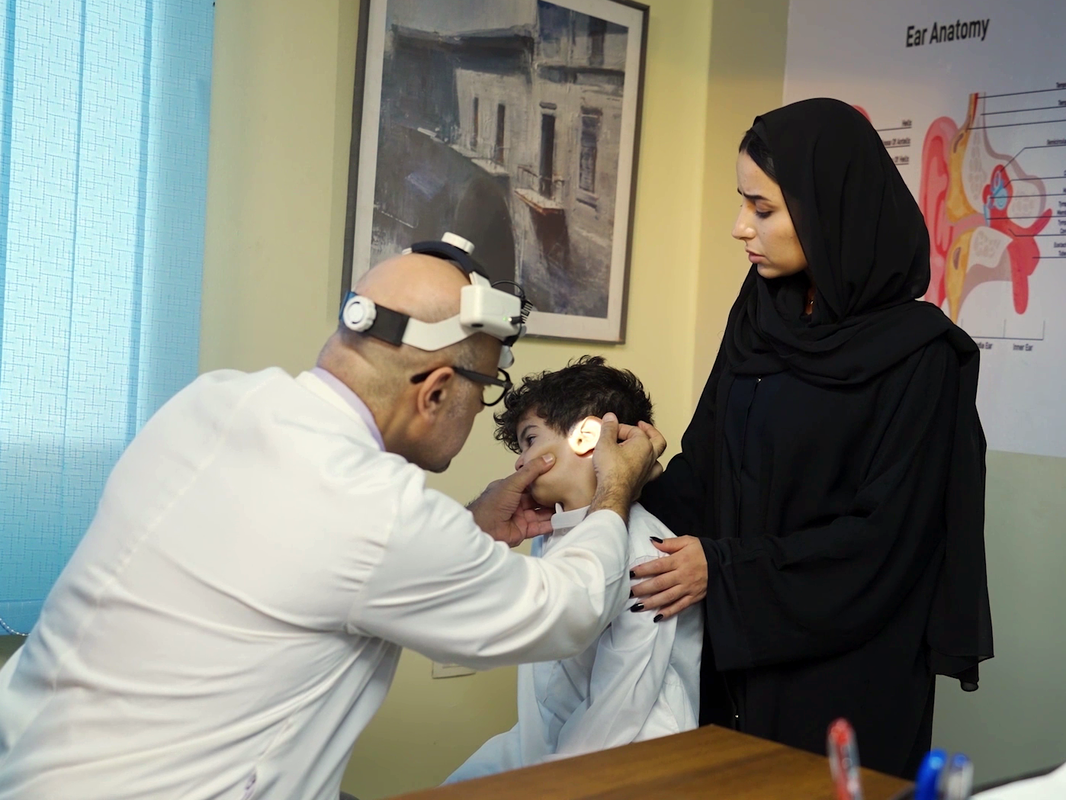
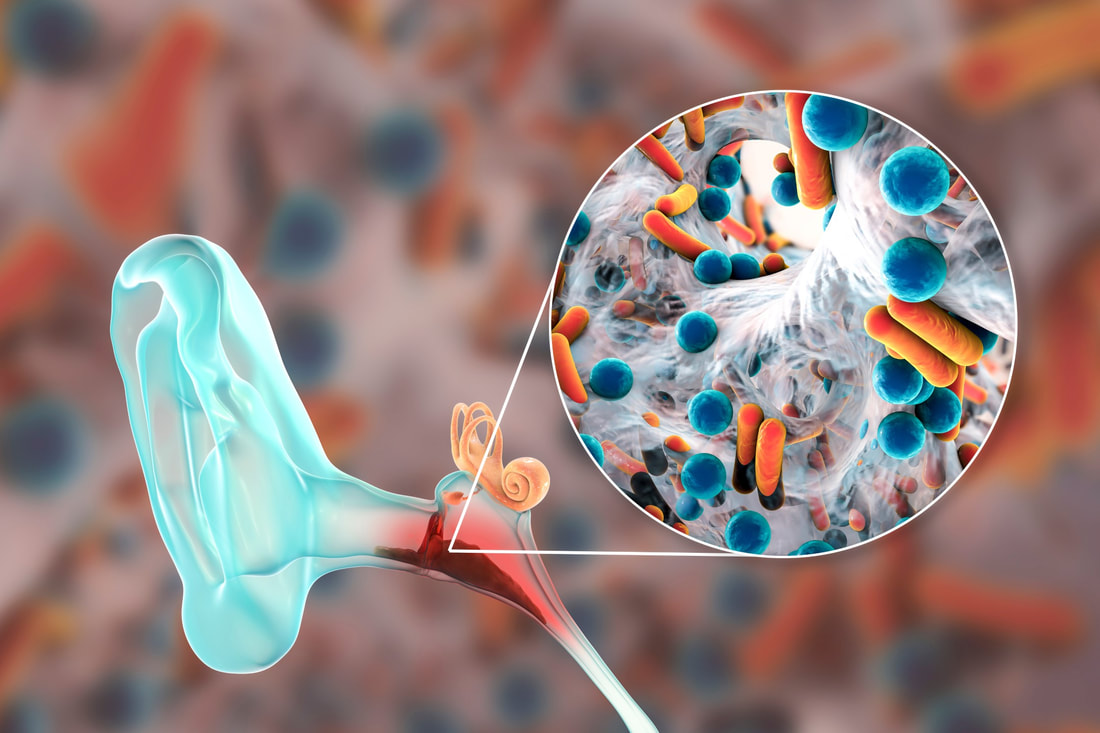
Acute Otitis Media From Theory to Practice
Acute otitis media is one of the most common childhood diseases, representing the most common indication for antibiotic prescription and outpatient visits in children.
More than 80% of children are affected by the age of 5 years. The aim of this module is to provide a review of acute otitis media epidemiology, its underlying pathophysiology, diagnosis, impact, preventive, and treatment options. Learning objectives: Upon successful completion of this module, you should be able to: 1. Identify and overview basic information about acute otitis media. 2. Describe the diagnostic approaches and management options for acute otitis media. 3. Examine the evidence beyond guideline recommendations for acute otitis media. 4. Apply acute otitis media guideline recommendations in the practical context. |
|
Acute Bacterial Rhinosinusitis Practice Essentials
Acute rhinosinusitis is one of the most frequently encountered conditions in primary care, and it is one of the most common reasons for antibiotic prescriptions. However, only a small proportion of viral sinus infections progress to acute bacterial rhinosinusitis, therefore antibiotics do not confer a distinct benefit in most acute rhinosinusitis cases. Accurate diagnosis and ensuring that only bacterial infections are treated with antibiotics are therefore vital for optimal management of acute bacterial rhinosinusitis.
The aim of this module is to provide you with practical knowledge about acute bacterial rhinosinusitis, its diagnosis, and management, in order to enhance patient care. Learning objectives: Upon successful completion of this module, you should be able to:
|
|
Tonsillopharyngitis Clinical Highlights
Tonsillopharyngitis or pharyngitis is one of the most frequent illnesses for which pediatricians, internists, and other primary care physicians are consulted.
Throughout this module, you will take an overview of tonsillopharyngitis as a disease. Further, you will recognize how to diagnose acute pharyngitis and different treatment regimens for it. Learning objectives: Upon successful completion of this module, you should be able to: 1. Describe tonsillopharyngitis disease. 2. Outline strategies for diagnosing tonsillopharyngitis. 3. Apply management guidelines for tonsillopharyngitis. 4. Consider the clinical evidence beyond guidelines. |
|
Community Acquired Pneumonia Clinical Pathway
Community-acquired pneumonia represents a daily challenge among physicians all over the world, in terms of clinical judgment, therapeutic management, and also when taking prognostic decisions with the resulting consequences.
The aim of this module is to review the basics of Community-acquired pneumonia; including its epidemiology, etiology, and diagnostic criteria, and explore guidelines for its clinical management, and the recommended preventive measures. Learning objectives: Upon successful completion of this module, you should be able to: 1. Outline basic information on community-acquired pneumonia. 2. Explore clinical practice guidelines for community-acquired pneumonia. 3. Identify community-acquired pneumonia diagnostic clues. 4. Develop a community-acquired pneumonia treatment plan based on clinical guidelines. 5. Describe the recommended preventive measures for community-acquired pneumonia. |
|
Assessing and Treating Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
COPD patients should have an assessment of the severity of their airflow obstruction, symptoms, history of exacerbations, exposure to risk factors, and comorbidities, to guide management.
In this module, you will explore tools to assess COPD, also, a personalized approach for starting treatment, based on level of symptoms and risk of exacerbation, as well as, supportive strategies to manage patients with stable COPD. Learning objectives: Upon successful completion of this module, you should be able to: 1. Discuss assessment and diagnosis of COPD. 2. Describe the management of symptomatic patients with stable COPD. 3. Explain supportive management strategies for patients with stable COPD. |
|
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Exacerbations
Exacerbations of COPD are important events in the management of COPD because they negatively impact health status, rates of hospitalization and readmission, and disease progression.
In this module, you will review the definition of acute exacerbations of COPD, as well, symptoms, triggers, and pathophysiology. Furthermore, you will explore the distribution patterns and consequences of these exacerbations on health and quality of life, for a better understanding of management, and different treatment options. Learning objectives: Upon successful completion of this module, you should be able to: 1. Explore a full overview required for a better understanding of acute exacerbations of COPD. 2. Assess the burden and risk factors for acute exacerbations of COPD. 3. Conclude the implications of acute exacerbations of COPD. 4. Figure out how to manage COPD exacerbations. |
|
COPD Treatable Traits
Reduction of current symptoms and future risks are the important goals for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease management. Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease implements three important steps to follow-up pharmacological management plan, which are, first, review, then assessment, and adjust if needed.
In this module, you will explore the treatment options for COPD according to Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease recommendations. Then, you will identify different studies to compare different treatment options and how to choose the best one for the patient. Moreover, the importance of adding inhaled corticosteroids to conventional treatment will be discussed. Learning objectives: Upon successful completion of this module, you should be able to:
|
|
Management of Symptomatic Asthma: Different Approaches and Outcomes
Well-controlled asthma can be achieved through various treatment regimens and
therapy options, each of which has different effects and outcomes. This module will discuss different asthma management approaches and how they reflect on patients’ quality of life, focusing on exploring regular inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) dosing, maintenance and reliever therapy (MART), and their real-world therapy outcomes. As well, long-acting muscarinic antagonists (LAMAs) and also their position in asthma management regimens. Learning objectives: Upon successful completion of this module, you should be able to: 1. Identify different symptomatic asthma treatment approaches. 2. Discuss regular ICS dosing, prescribing confusion, and perception in asthma control. 3. Compare management outcomes for regular ICS dosing and MART. 4. Develop an asthma treatment plan appropriate for your patient. |
|
Pharmacological Treatment Options for Managing Asthma
Asthma is one of the most common chronic inflammatory disorders, for which many
treatment options are available. These therapy options have different indications and outcomes. The aim of this module is to review different pharmacological treatment options for asthma. For this educational purpose, this module will discuss treatment goals, treatment guidelines, and the role of inhaled corticosteroids in asthma management. Learning objectives: Upon successful completion of this module, you should be able to: 1. Recognize asthma treatment goals. 2. Explain the role of inflammation in asthma pathophysiology. 3. Develop an asthma treatment plan based on the Saudi initiative for asthma approach. 4. Explore the importance of regular inhaled corticosteroids in asthma management. 5. Outline safety considerations regarding inhaled corticosteroids use. |
|
Acute Asthma Exacerbations In Adults
Asthma exacerbations are a serious global health problem affecting all age groups. Its
prevalence is increasing in many countries. Asthma exacerbations still impose an unacceptable burden on health care systems, and on society through loss of productivity in the workplace and disruption to the family. In this module, you will explore an overview of asthma exacerbations, their impact, and management. Learning objectives: Upon successful completion of this module, you should be able to: 1. Clarify asthma exacerbations definition, prevalence, and pathophysiological effects. 2. Outline severity and impact of asthma exacerbations. 3. Illustrate the management approaches of asthma exacerbations. 4. Apply hypothetical case studies that reflect real-world experience. |
|
Antimicrobial Resistance: A Global Public Health Threat
The rapid emergence of resistant bacteria is occurring worldwide, endangering the efficacy of antibiotics, which have transformed medicine and saved millions of lives. Antibiotic drug consumption is a major driver of antibiotic resistance. Within just a few years, we might be faced with a big problem, medically, socially, and economically, unless real and unprecedented global coordinated actions are immediately taken.
The main objective of this module is to shed light on the global emerging threat of antimicrobial resistance that is really endangering the efficacy of the currently used antibiotics. Learning objectives: Upon successful completion of this module, you should be able to:
|
|
Fundamentals of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a common and treatable disease characterized by progressive airflow limitation and tissue destruction. COPD causes persistent and progressive respiratory symptoms, including difficulty in breathing, cough, and or phlegm production. Environmental exposure to tobacco smoke, indoor air pollution, and occupational dust, fumes, and chemicals are important risk factors for COPD.
The main objective of this module is to shed light on the basic information about COPD and its pathophysiology. Learning objectives: Upon successful completion of this module, you should be able to: 1. Recall the basic knowledge about COPD. 2. Explain the pathophysiology of COPD. 3. Discuss the burden of COPD. |
|
Adult Asthma: Introduction, Prevalence and Burden
Asthma is a common lung condition that causes occasional breathing difficulties. However many people think of asthma as a childhood illness, adults can also develop asthma and may experience asthma for the first time as an adult. There has been a sharp increase in the global prevalence, morbidity, mortality, and economic burden associated with asthma over the last 40 years. In this module, you will explore an overview of asthma, its prevalence, and burden.
Learning objectives: Upon successful completion of this module, you should be able to: 1. Recall the basic knowledge about asthma. 2. Explore the prevalence of asthma both globally and in KSA. 3. Conclude the overall health burden of asthma. 4. Distinguish between the direct and indirect economic burden of asthma. |
|
Assessing and Treating Stable Asthma
Asthma is a chronic condition that affects the airways. An asthma diagnosis and
assessment are based on several factors, including a detailed medical history, symptoms, and overall health and test results. In this module, we discuss asthma diagnosis, assessment, and aspects for consideration with commonly used inhaler devices, including metered-dose inhalers, dry powder inhalers, and other types of inhalers. Learning objectives: Upon successful completion of this module, you should be able to: 1. Recognize how an asthma diagnosis is established. 2. Assess the patient’s level of asthma control. 3. Guide your patient to achieve good asthma control. 4. Identify different asthma medications. 5. Assign the challenges of inhaler selection and adherence. |
|
Exercise-Induced Bronchoconstriction in Patients with Asthma
Exercising regularly has a wide range of beneficial health effects; in particular, it has
been well documented to help in the management of chronic illnesses including asthma. However, in some individuals, exertion can also trigger an exacerbation of asthmatic episodes and subsequent acute attacks of breathlessness, coughing, tightness of the chest, and wheezing. This physiological process is called exercise-induced bronchoconstriction (EIB). In this module, you will learn more information about exercise-induced bronchoconstriction including prevalence and burden, pathophysiology, symptoms and different triggers, as well diagnostic tools and challenges for a better understanding of managing EIB. Learning objectives: Upon successful completion of this module, you should be able to: 1. Define exercise-induced bronchoconstriction (EIB). 2. Conclude prevalence and burden of EIB. 3. Recognize the pathology of EIB. 4. Discuss different triggers and accompanying symptoms of EIB. 5. Interpret diagnostic tools supporting the implementation of a treatment plan for EIB. |
|
Severe Asthma
Patients with severe asthma represent a major unmet need, as they experience
frequent exacerbations, are hospitalized more often, and utilize the majority of health care expenses in asthma. In this module we will explore severe asthma definition, impact, pathophysiology and management. Learning objectives: Upon successful completion of this module, you should be able to: 1. Clarify severe asthma definition and its burden. 2. Explain the pathophysiology of severe asthma. 3. Discuss diagnosis, phenotyping, and endotyping. 4. Plan management of severe asthma. |
|
Recommendations for Improving Allergic Rhinitis Control
Allergic rhinitis (AR) is a high-prevalence disease. Patients may miss work because of
symptoms or it leads to reduced workplace productivity. In addition, asthma and AR frequently co-exist, with epidemiological data suggesting that most asthma patients also suffer from AR. This learning track suggests effective control of AR, focusing on patient preferences which may play a role in enhancing treatment compliance and affect patients' willingness to adhere to therapy. Recommendations from guidelines are discussed in this module as well, aiming to reflect a better real-life care. Learning objectives: Upon successful completion of this learning track, you should be able to: 1. Recall the signs and symptoms of AR. 2. Discuss the prevalence and socioeconomic burden of AR. 3. Explain strategies used to control AR and its comorbidities. 4. Evaluate evidence for the AR treatment options based on patient satisfaction and preference. 5. Describe recommendations from evidence-based guidelines for controlling AR. |
|
Anti-infective
This learning track aims to provide an overview of some common infectious diseases
that affect children and adults, such as acute otitis media, acute bacterial rhinosinusitis, tonsillopharyngitis, and community-acquired pneumonia. It will cover the epidemiology, etiology, pathophysiology, diagnosis, impact, prevention, and treatment of these diseases, with a focus on the appropriate use of antibiotics and the global threat of antimicrobial resistance. It will also review the current guidelines and recommendations for the clinical management of these diseases and the best practices to enhance patient care and outcomes. Learning objectives: Upon successful completion of this learning track, you should be able to: 1. Describe the epidemiology, etiology, pathophysiology, diagnosis, impact, prevention, and treatment of acute otitis media, acute bacterial rhinosinusitis, tonsillopharyngitis, and community-acquired pneumonia. 2. Identify the common causative agents and risk factors for these infectious diseases. 3. Apply the current guidelines and recommendations for the clinical management of these diseases, including the appropriate use of antibiotics and the assessment of severity and prognosis. 4. Recognize the global threat of antimicrobial resistance and its implications for patient care and public health. 5. Evaluate the effectiveness and safety of different preventive and therapeutic interventions for these diseases. 6. Demonstrate the best practices to enhance patient education, communication, and adherence to treatment. |
|
COPD
This learning track aims to provide an overview of chronic obstructive pulmonary
disease (COPD), a common and treatable disease characterized by progressive airflow limitation and tissue destruction. It will cover the basic information about COPD and its pathophysiology, risk factors, symptoms, and impact. It will also review the tools and guidelines for assessing and managing COPD, including the pharmacological and non- pharmacological interventions, the prevention and treatment of exacerbations, and the follow-up and adjustment of the treatment plan. It will also discuss the latest evidence and recommendations for the optimal management of COPD and its comorbidities. Learning objectives: Upon successful completion of this learning track, you should be able to: 1. Describe the basic information and pathophysiology of COPD. 2. Identify the risk factors, symptoms, and impact of COPD on health and quality of life. 3. Apply the tools and guidelines for assessing the severity and prognosis of COPD, including spirometry, symptom scales, and exacerbation history. 4. Select the appropriate pharmacological and non-pharmacological interventions for managing stable COPD, based on the level of symptoms and risk of exacerbations. 5. Recognize the definition, triggers, and consequences of acute exacerbations of COPD, and the strategies to prevent and treat them. 6. Review the follow-up and adjustment of the treatment plan for COPD, according to the response and adherence of the patient. 7. Evaluate the latest evidence and recommendations for the optimal management of COPD and its comorbidities. |
|
Asthma: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Management
Asthma is a common and chronic lung condition that affects the airways and causes breathing difficulties. It can occur in adults and children and has a significant impact on health and quality of life. This learning track covers various topics related to asthma, such as its prevalence, burden, diagnosis, assessment, treatment options, management approaches, and therapy outcomes. It also discusses the role of different inhaler devices and medications, such as inhaled corticosteroids, maintenance and reliever therapy, and long-acting muscarinic antagonists. You will learn about the current guidelines and best practices for asthma care.
Learning objectives: Upon successful completion of this learning track, you should be able to: Define the basic concepts and terminology related to asthma. Describe the prevalence and epidemiology of asthma globally and in KSA. Analyze the health and economic burden of asthma on individuals and society. Compare and contrast the direct and indirect costs of asthma. Explain how to diagnose asthma based on medical history, symptoms, and tests. Evaluate the level of asthma control in patients using validated tools. Apply the principles of patient education and self-management to achieve good asthma control. Classify different types of asthma medications and inhaler devices according to their mechanism of action and indications. Identify the challenges and barriers to inhaler selection and adherence in patients with asthma. Formulate an individualized asthma treatment plan based on the Saudi initiative for asthma guidelines and patient preferences. |
|
Managing Asthma in Different Settings: From Exercise Passing by Exacerbations Up to Severe Cases
Asthma is a chronic condition that affects the airways and causes breathing difficulties. It can be triggered or worsened by various factors, such as exercise, allergens, infections, or stress. Some people with asthma have more severe symptoms and frequent exacerbations that require hospitalization and intensive treatment. In this learning track, you will learn about the different types of asthma, such as exercise-induced bronchoconstriction (EIB), acute exacerbation asthma, and severe asthma in terms of their prevalence, impact, pathophysiology, diagnosis, and management.
Learning objectives: Upon successful completion of this learning track, you should be able to: Define exercise-induced bronchoconstriction (EIB) and asthma exacerbations, and explain their prevalence, burden, pathophysiology, and mechanisms among different populations. Identify the common triggers and symptoms of EIB and asthma exacerbations and how they affect exercise performance, quality of life, and health outcomes. Describe the diagnostic tools and methods for EIB and asthma exacerbations and their advantages and limitations. Develop a treatment plan for EIB and asthma exacerbations based on the patient’s needs, preferences, goals, and severity. Apply the principles of asthma exacerbation management, including prevention, early recognition, treatment, and follow-up. Solve hypothetical case studies that reflect real-world scenarios of EIB and asthma exacerbation management. Define severe asthma and its burden on patients and society, and explain the pathophysiology and the role of phenotypes and endotypes in its classification and treatment. Describe the diagnosis, assessment, and monitoring of severe asthma using various tools and biomarkers. Formulate a management plan for severe asthma based on the current guidelines and evidence-based interventions. |
|
Introduction to Vaccination
In this module, we will provide an overview of the purpose of this program and how the vaccine is critically important for our society and the role of healthcare workers in providing evidence-based advice.
Learning Objectives: By the end of this module, you should be able to: -Define the role of The Primary Care Physicians, GPs, nurses and pharmacists in Disease Prevention and raising the awareness about the importance of immunization - List the common misconceptions regarding vaccinations, and the scientific evidence to dispel them - List some vaccine-preventable diseases - Explain the importance of vaccination in disease prevention |
|
Vaccination Procedures & Vaccine Safety
In this module, you will learn how to maintain the quality of vaccines throughout the cold chain, how to prepare and administer vaccines according to best practice, how to follow correct vaccination procedures to ensure safety and effectiveness, and how to communicate with vaccine recipients or carers and help them make informed decisions.
Learning Objectives: By the end of this module, you should be able to: • Mention the vaccine administration procedures and protocols to ensure the safe administration of the vaccines. • List the needed vaccine handling and storage main requirements to maintain the quality and potency of vaccines. • List the most common adverse events following vaccination and the main contraindications. |
|
Common Vaccination Errors and How to Avoid Them
In this module, you will learn about the common vaccination errors and how to prevent them, the common myths and misconceptions about vaccination and how to refute them with scientific evidence, and the importance of providing accurate and reliable information as a healthcare worker.
Learning Objectives: By the end of this module, you should be able to: • Describe common vaccination errors and best practices to avoid them. • Recall common misconceptions regarding vaccinations, and the scientific evidence to dispel them. • Recognize the importance of correct scientific information and the role of healthcare workers. |
|
Opportunities for Vaccination
In this module, you will learn about the main factors that influence vaccine hesitancy and how to use them to encourage vaccine acceptance, the best practices to increase the chances of vaccination, and how to communicate more effectively and confidently with caregivers and vaccine recipients in your daily work.
Learning Objectives: By the end of this module, you should be able to: - List the reasons for vaccine hesitancy among patients and healthcare professionals - List the common misconceptions regarding vaccinations, and the scientific evidence to dispel them. |
|
Facts About the Adult Tadp Vaccine
Tdap is a combination vaccine that protects against three potentially life-threatening bacterial diseases (Tinnitus, Diphtheria, and Pertussis).
In this module, you will recognize the importance of administering the vaccine in the face of these 3 diseases. Learning Objectives: Upon completion of this module, you should be able to: • Determining the important role of Tdap vaccine against tetanus, diphtheria, and pertussis. • Clarification of the immunization schedule. • Explain the side effects of the vaccine. • Illustrate who should and should not get the vaccine. • Explain the importance of the vaccination center. |
|
Pertussis: Current Status and Prevention
The aim of this module is to update your knowledge about pertussis pathophysiology, diagnosis, and prevention. Furthermore, the management of pertussis in different populations will be highlighted.
Learning Objectives: Upon completion of this module, you should be able to: • Describe pertussis pathophysiology and causative agent. • Identify individuals at high risk of infection and complications. • Implement accurate diagnosis, management, and prevention strategies. • Choose effective treatment regimens for each category of patients. • Participate in active and accurate surveillance for pertussis. |
|
Diphtheria Perception and Principles
In this module, you as a healthcare professional will explore the etiology, epidemiology, pathophysiology, clinical features, diagnosis, and management of this highly contagious disease and you will be able to plan how to prevent it.
Learning Objectives: Upon completion of this module, you should be able to: • Explore the etiology and epidemiology of diphtheria. • Outline risk factors and pathophysiology of diphtheria. • Utilize the clinical findings and laboratory investigations in the diagnosis of diphtheria. • Construct treatment and prevention approaches for diphtheria. |
|
Understanding Tetanus Infection
This module aims to develop the knowledge of tetanus diagnosis and treatment and prevention,
you as a healthcare practitioner can develop hygienic surgical practice and provide awareness towards tetanus disease. Learning Objectives: • Upon completion of this module, you should be able to: • Outline the etiology and pathophysiology of tetanus infection. • Define the appropriate diagnosis for tetanus infection. • Explain hygienic circumcision after birth. • Identify surveillance systems and awareness regarding tetanus. |
|
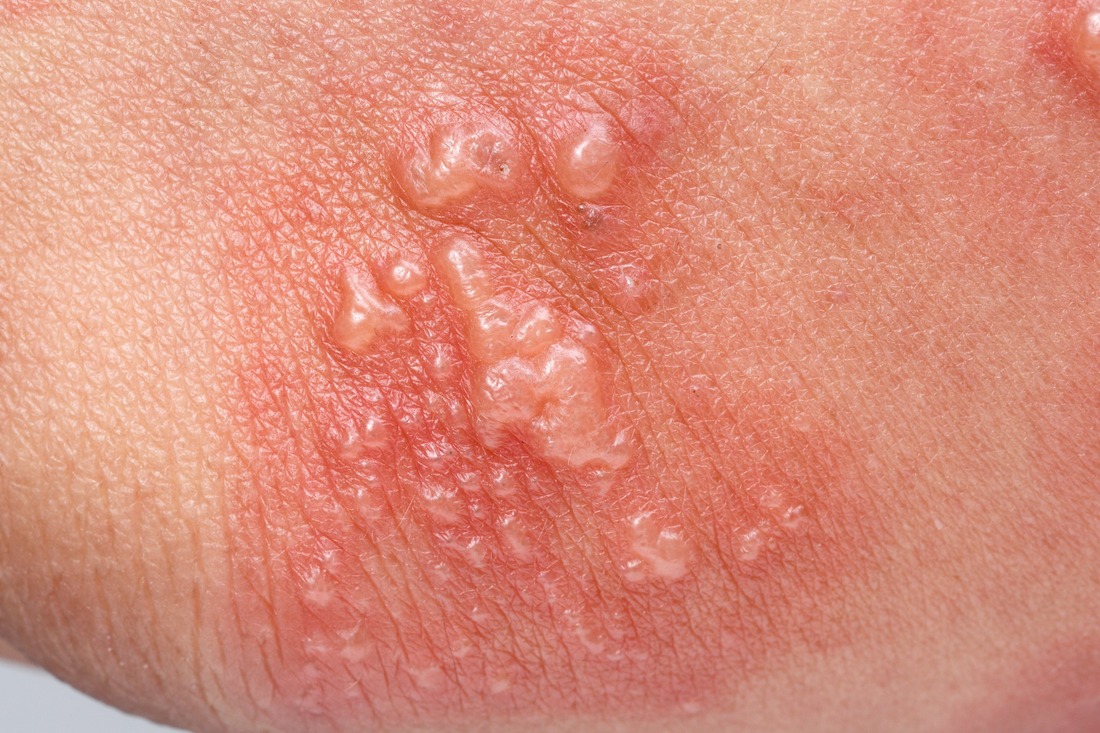
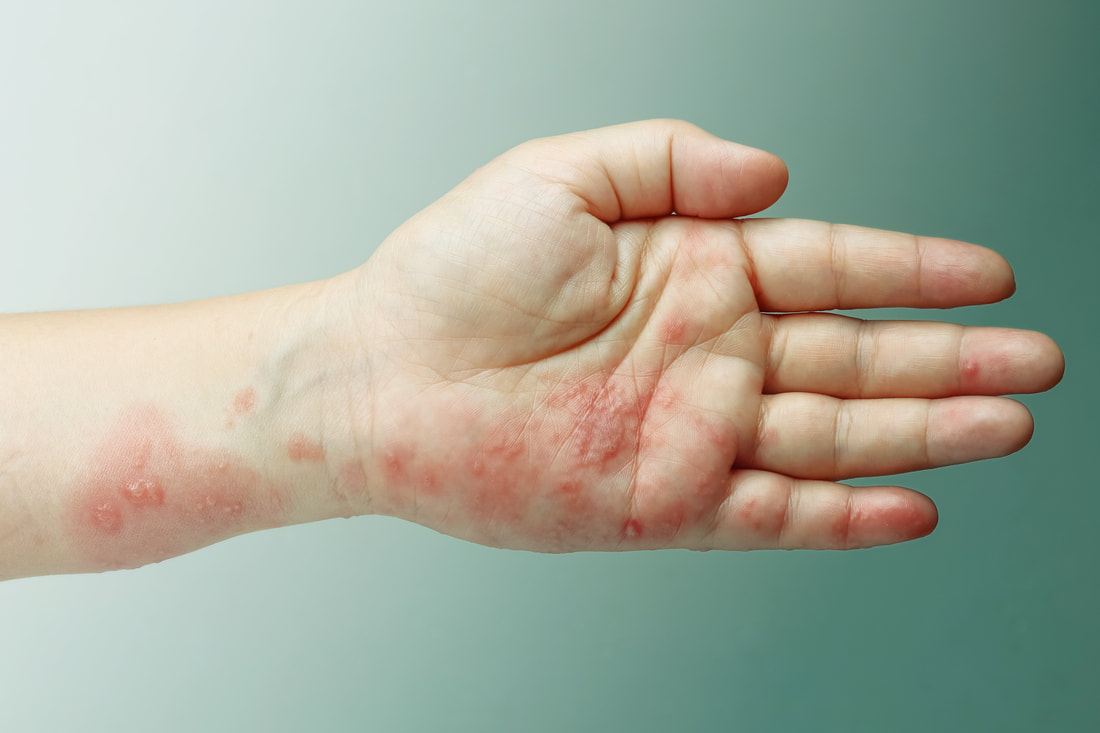
Shingles A Dermatological Perspective
We’ll talk about the presentation, evaluation, and management of herpes zoster and focus on the clinical severity of herpes zoster, including its morbidity and complications.
Learning Objectives: Upon completion of this video, you should be able to: • Describe the clinical presentation of a patient with herpes zoster and identify various clinical presentations of it. • Evaluate the herpes zoster rashes and other symptoms. • Discuss the severity of symptoms and complications of herpes zoster in immunocompromised patients. • List management options available for herpes zoster. • Discuss the recurrence of herpes zoster and how to manage it. |
|
Shingles Neurological Perspective
Herpes zoster (shingles) is caused by the reactivation of varicella-zoster virus (VZV), and painful blistering occurs when VZV cell-mediated immunity wanes with age or is immunocompromised.
In this video, you will learn more about herpes zoster complications, causes, management, and prevention options. Learning Objectives: Upon completion of this video, you should be able to: • Discuss the neurological complications of herpes zoster. • List the causes of postherpetic neuralgia (PHN). • Discuss the impact of postherpetic neuralgia on the quality of life. • Identify the management options for herpes zoster complications. • Recognize the options for prevention. |
|
Age Related Decline in Immunity (ARDI) and Shingles Disease
Vaccine responses and aging is a topic that examines how the immune system declines with age and how that affects vaccine efficacy in older adults.
In this video, we will discuss how to improve vaccination outcomes in older adults by using different types of vaccines and vaccination strategies. Learning Objectives: Upon completion of this video, you should be able to: • List and compare the similarities and the differences in vaccine responses based on age and how adults respond to various types of vaccines • List the age-related defects in T cells and discuss how that affects primary vaccine response. • Define and mention the ways in which aging affects the functionality of the B-cell compartment. • Mention the different vaccination strategies that can be used to overcome deficiencies of vaccine responses in the aging immune system. |
|
Herpes Zoster The creeping Foe
Despite the prevalence of herpes zoster and the availability of a vaccine for more than a decade, its vaccination rates remain strikingly low. In order to reduce the disease burden, healthcare practitioners must remain up to date on all aspects of disease prevention and management.
This video discusses the disease burden, and overall health impact of herpes zoster, epidemiology, clinical presentation and diagnosis, management, and prevention strategies. Learning Objectives: Upon completion of this video, you should be able to: • Explain the risk factors, epidemiology, disease burden, and overall health impact of herpes zoster. • Summarize the pathophysiology and complications of herpes zoster. • Identify various clinical presentations of herpes zoster. • Apply strategies for herpes zoster prevention. • Conduct an appropriate diagnostic assessment that addresses a valid differential diagnosis. • Construct an evidence-based treatment plan that correctly addresses potential complications. |
|
Pharmacist Role and Special Population Nutrition
In this module, we’ll talk about consultation and recommendation of nutritional supplements. Moreover, special population micronutrients consideration, also specific organ micronutrients consideration, and finally, we’ll talk about specific states of micronutrient consideration.
Learning objectives: Upon completion of this module, you should be able to:
|
|
Understanding the Difference between Macronutrients vs. Micronutrients
Nutrition is essential to our health, so we will discuss macronutrients and micronutrients containing vitamins and minerals. The aim of this study is to determine the important role of micronutrients and macronutrients for all vital functions of the body. As a community pharmacist, you can assign the visitor essential nutrition for living a good lifestyle.
Learning objectives: Upon completion of this module, you should be able to:
|
|
Understanding Immune System and Its Relation to Nutrition
The aim of this module is to develop the link between immunity and nutrition, you as a community pharmacist can define nutrient needs for a healthy lifestyle.
So, in this module, we’ll talk about the introduction to immunity, moreover, enhancing the immune system, furthermore, the link between immunity and nutrition, and finally basics of nutrients and metabolism. Learning objectives: Upon completion of this module, you should be able to:
|
|
Smoking Quitting: A Practical Plan for Your Patient
Tobacco use can lead to tobacco dependence and serious health problems. Quitting smoking greatly reduces the risk of developing smoking-related diseases.
Throughout this module, you will explore general knowledge about how to tailor a plan for smoking quitting for each patient, as well as identify the role of different healthcare professionals in smoking quitting. Moreover, you will explore the role of community and non-profit organizations in helping patients to quit smoking. Learning objectives: Upon completion of this module, you should be able to:
|
|
Pharmacological and Non-pharmacological Interventions for Smoking Cessation
Nicotine replacement therapy (NRT) is a treatment to help people stop smoking. It uses products that supply low doses of nicotine.
Throughout this module, you will explore non-pharmacological interventions for smoking cessation, different types of NRT, and how it works in smoking quitting. Furthermore, you will learn the advantages and disadvantages of NRT. Also, you will discover other non-nicotine-based options and their mechanisms of action. Finally, we will take a quick look at combination treatment. Learning objectives: Upon completion of this module, you should be able to:
|
|
Smoking Cessation between Opportunities and Challenges
Quitting smoking lowers the risks of several diseases and improves the quality of life.
Throughout this module, you will recognize the benefits of quitting smoking. Then, you will find out the causes of nicotine dependence and how to overcome it. Moreover, you will know the causes of relapse and how to prevent it. Learning objectives: Upon completion of this module, you should be able to:
|
|
Epidemiology of Smoking
Smoking tobacco is a major health problem and an important cause of premature death worldwide. It causes a wide range of diseases, including many types of cancer, chronic respiratory diseases, coronary heart disease, stroke, and erectile dysfunction.
Through this module, you will explore the history of smoking. As well, the different types of tobacco products. Moreover, you will be able to know the diseases correlated with smoking and other consequences on lifestyle. After that, you will be able to understand the misconception of E-cigarettes. Learning objectives: Upon completion of this module, you should be able to:
|
|
Tdap - It's Time to Give an Extra Booster!
Tetanus, diphtheria, and pertussis are three bacterial diseases that can cause severe complications in the nervous, respiratory, and immune systems. Tetanus causes painful muscle contractions, diphtheria causes a thick membrane in the throat and nose, and pertussis causes violent coughing.
They can be detected by clinical features and laboratory tests, and treated in different ways. They can be prevented by vaccination with the Tdap vaccine, which protects against all three infections. Learning Objectives: By the end of this track, you should be able to: • Explore the etiology, pathophysiology, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of diphtheria. • Outline the etiology, pathophysiology, and diagnosis of tetanus infection. • Conduct surveillance systems and awareness regarding tetanus. • Describe pertussis pathophysiology and causative agent. • Identify individuals at high risk of infection and complications and choose the appropriate treatment for each category. • Implement accurate diagnosis, management, and prevention strategies for pertussis. • Determine the role of the Tdap vaccine against tetanus, diphtheria, and pertussis. |
|
Shingles Prevention and Management
Shingles are a serious condition that can cause lasting pain and complications. It can be prevented by vaccination, which is recommended for people at different ages and risk groups. Education and awareness are key to preventing and managing shingles.
Learning Objectives: By the end of this track, you should be able to: • Explain the epidemiology, pathogenesis, pathophysiology, clinical stages, presentation, and diagnosis of shingles. • Identify the risk factors, complications, and management options of shingles. • Define the importance of healthcare practitioners’ and patients’ education to manage shingles symptoms and improve the quality of life. • Define what is life-course immunization and recognize how it can help with shingles prevention. • List the types, indications, safety, efficacy, recommendations, and misconceptions of shingles vaccine. |
|
Shingles - Experts Insights
In this track, we will talk about the risk factors, symptoms, epidemiology, pathophysiology, diagnosis, management, prevention, and complications of herpes zoster, as well as the vaccine responses and severity in different age groups and immune statuses. And we will discuss how to evaluate herpes zoster rashes and other symptoms, and how to identify the neurological complications of herpes zoster, and the management options for these complications.
Learning Objectives: By the end of this track, you should be able to: • Explain the risk factors, symptoms, epidemiology, pathophysiology, and diagnosis of herpes zoster. • Apply strategies for herpes zoster management and prevention. • Discuss the neurological complications of herpes zoster and the management options for these complications. • Describe the differences in vaccine responses based on age and how older adults respond to various types of vaccines. • Evaluate the herpes zoster rashes and other symptoms. • Discuss the severity of symptoms and complications of herpes zoster in immunocompromised patients. |
|
Meningitis-Serogroup B Vaccine Close the Loop
Meningitis is a serious infection of the meninges that can be caused by various pathogens. Some of these pathogens can be prevented by vaccination, which is an important strategy for reducing the morbidity and mortality of meningitis.
In this track, you will learn about the different types of vaccine-preventable meningitis, its diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. Learning Objectives: By the end of this track, you should be able to: • Summarize the classifications of meningitis. • Review the causes and risk factors of meningitis. • List the most common pathogens causing infectious meningitis. • Identify the distribution of pathogens causing infectious meningitis. • Highlight the potential risk of meningococcal meningitis in high-risk groups, disease outbreaks, and epidemiology data, in Saudi Arabia and worldwide. • Recognize the pathogenesis and pathophysiology of meningococcal meningitis and their differences from other vaccine-preventable meningitis. • List the clinical manifestations of meningococcal meningitis and discuss their diagnostic utility. • Apply the diagnostic procedures of meningococcal meningitis and summarize their use in the differential diagnosis. • Recall the risk factors in developing meningococcal meningitis complications, list those complications, and recognize the differences from other forms of vaccine-preventable meningitis. • Discuss the importance, barriers, warnings, and precautions of meningococcal vaccination. • Identify available meningococcal vaccines in Saudi Arabia. • Choose an appropriate vaccine for each patient according to his age, health condition, and situation. • Apply vaccine recommendations properly. |
|
Ensure Vaccine Safety, Potency, and Administration
This track should help you learn about the importance, principles, and challenges of vaccination, and how to communicate effectively with vaccine recipients and caregivers.
Learning Objectives: By the end of this track, you will be able to: • Recognize the benefits of vaccination for individuals, communities, and society. • Explain how vaccines work and stimulate the immune system. • Identify the different types of vaccines and their components. • Describe common vaccination errors and best practices to avoid them. • Recall common misconceptions regarding vaccinations, and the evidence to dispel them. • Conclude common vaccine safety concerns and the available evidence. • Identify different types of adverse events following immunization. • Recognize the importance of vaccine safety measures and surveillance. • Describe the factors that influence vaccine hesitancy and acceptance. • Lead confident and respectful conversations about vaccination. |
|
Optimization of Oral Glucose-lowering Agents for The Management of Type 2 Diabetes
In this module, we will explore how oral glucose-lowering agents are essential to prevent type 2 diabetes complications and how to personalize the treatment to achieve the best clinical outcome considering the guidelines’ recommendations.
|
|
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus- Clinical Cases
According to what you have learned in previous modules, you will discover what is the ideal add-on drug, identify how to personalize the management needed, figure out what is the ideal 3rd add-on drug, and evaluate the risk stratification and decide the dose modifications needed.
|